Understanding HotStuff and Byzantine Fault Tolerance 🤖
Disclaimer: All opinions of the author are their own
🎃 Hi everyone 😊
This post explores the importance of consensus in maintaining data integrity and how HotStuff has revolutionized the field of distributed computing. Are you ready?
This post will answer three important questions: — What is the Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus problem, and how does HotStuff solve it? — How does HotStuff compare to other consensus algorithms used in blockchain technology? — What are some real-world applications of HotStuff and its consensus algorithm?
Let’s dive in! I am so excited my dear readers 🚨
The Byzantine Generals Problem 🌋
The Byzantine Generals problem is a well-known metaphor for a critical problem in computer science, specifically distributed computing systems. In such scenarios, several machines (nodes) have to agree on a specific state or decision, even if some of the nodes may be faulty or malicious.
I’m sure you know about this problem, but still, I want to explain it so it is fresh in your mind 🙂
Imagine several generals, each leading a portion of the Byzantine army! They are preparing to attack a city but must coordinate their attack to succeed. The generals are situated at different locations around the city and send messages to each other to plan their attacks.
However, the generals face additional uncertainties that complicate their attack:
🔵 Some generals might be traitors and might try to sabotage the attack.
🔵 The messages could be intercepted or manipulated.
To succeed, the loyal generals must agree on a common strategy they can successfully coordinate together even with the unreliable generals. Their strategy is known as consensus and it’s ability to succeed is known as fault tolerance. The crux of this question is:
How can they achieve consensus even when some generals may be traitors?
It’s crucial in systems where consistency is vital, and errors or malicious behavior could lead to severe consequences, such as in financial systems, safety-critical systems, and blockchain networks.
Now that we understand the Byzantine General’s Problem is, let’s move on!
Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) 🛎
Allow me to break down the Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) and the HotStuff consensus protocol in an easy-to-understand way! :)
Byzantine Fault Tolerance is a property of a network system that allows the network to work correctly and reach consensus even if some of its components are failing or acting in a way that is not predictable, erratic or malicious. These unpredictable, erratic, or malicious components are known as Byzantine Faults.
Here is an analogy that will clear this up for you my dear reader🌝
Imagine you and your friends are organizing a surprise birthday party for your girlfriend.
👫 You’re trying to pick the day and time for the party, and you can only communicate through group chats. Everyone needs to agree on single time for the party to be successful.
Now, let’s suppose one member of the group starts behaving erratically, they are really crazy man!🤓
Frustrating, right? How are you supposed to coordinate a successful party when you are working with such an erratic friend?
You need a mechanism that ensures that even when there is one or more party behaving in a “Byzantine” manner, the group can still reach consensus or agreeement.
This is why the Byzantine Fault Tolerance so important in distributed computing.
So, in summary: in a distributed system, which is a group of networked computers working together, a Byzantine Fault is any situation where a computer does not follow the standard protocol due to errors, network issues, or malicious intent.
We say, a system is Byzantine Fault Tolerant if it can still function correctly and reach full consensus, and agree on the same value, despite these faults in the network.
Now if you understand the Byzantine Generals Problem and Byzantine Fault Tolerance, I will tell you about another subject. Are you ready? I wish you could see how excited I am about this topic. 😊

The HotStuff Consensus Protocol🎈
HHotStuff is one example of a Byzantine Fault Tolerant consensus protocol. This mechanism was developed to handle scenarios just like the one described above but specifically for blockchain systems, which are systems where there are many different computers, also known as nodes, and each of these nodes must agree on the state of the blockchain together, or form consensus.
The protocol was developed by VMware Research, a research group with expertise in distributed systems, computer architecture, and algorithms. This group forms the basis of Facebook’s Diem blockchain consensus protocol. Let’s return to our birthday party analogy. Woohoo!
With HotStuff, the process might look like this:
The process repeats for each new decision that needs to be made. I love this process, it is my favorite! ❤️
If the leader starts behaving erratically, just like our Byzantine friend from before, then a new leader will be chosen. This way, even if there is an unpredictable amount of unpredictable people who may unpredictably try to sabotage the party plans, the group can still successfully agree on a date.
In the context of blockchains, each “decision” by the party is akin to a new block added to the chain. So instead of people, there are Nodes, and these nodes propose, vote on new blocks, and then confirm these proposals as the addition of new block to the blockchain. This process ensures that even if some of the nodes are acting in a Byzantine manner, that is some of the nodes are behaving unpredictably or erratically, then the blockchain can still remain consistent and reliable as long as more than two-thirds of the nodes are honest.
It is a lot of information, let me break it down for you my dear reader. The core concept behind the HotStuff consensus protocol is: a secure, efficient way to make sure that a group can reach agreement, even when some members of the group are not behaving as expected.
This is, of course, a simplified version of how it works, but I am sure it will give you a good introduction to Byzantine Fault Tolerance and HotStuff!
I hope this is a worthy explanation for you my dear reader, but, if you do not understand, do not hesitate to get in touch with me. I love to talk!
Here’s a quick summary
Please allow me one moment my dear reader. I want to summarize the information I just shared above.
✅ The BFT consensus problem is a challenge in distributed computing where a group of nodes must agree on a value or decision, despite the possibility that some nodes may be faulty or malicious.
✅ This consensus problem may be difficult as errant or malicious nodes may try to disrupt the consensus process by sending conflicting information or by witholding information all together.
✅ HotStuff is a consensus algorithm that solves the BFT consensus problem by introducing a new approach to viewing synchronization. In traditional BFT algorithms, viewing synchronization can be slow and resource-intensive, which makes it difficult to reach a consensus.
✅ HotStuff’s Pacemaker Module helps networks solve this challenge by offering a separate module focused on appearance synchronization.
✅ HotStuff also introduces a new approach to block validation that helps ensure that all nodes have the opportunity to participate in the consensus process.
✅ By introducing deadlocks and delays to the process, HotStuff helps ensure that all nodes can participate and reach agreement before taking the next step.
Overall, HotStuff is a major breakthrough in reaching consensus on distributed systems.
HotStuff is an innovative approach to viewing synchronization and block verification, which makes it an essential tool for developers working with distributed systems, including blockchains.
Now, that you have this background, and have a basic understanding of the Byzantine Generals Problem, Byzantine Fault Tolerance, and the solutions provided by HotStuff, I would like to explain and summarize an article written by a computer scientist that I am very fond of. Follow her here my dear readers.
Now, I would like to explain and summarize an article written by a computer scientist that I am very fond of. Follow her here my dear readers.
The “Preliminaries” section provides some background information about the problem HotStuff is designed to solve! Like what?
This section discusses the Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus issue. They explain that in daily replication, a group of nodes must agree on a growing set of values called “blocks”.
Overall, the “Preliminaries” section provides an important context that helps readers understand the challenges HotStuff is designed to address. There are introductions to key concepts such as log replication and partially concurrent settings, concepts, which together help readers understand why it can be difficult to reach consensus in distributed systems and why innovative solutions like HotStuff are so important.
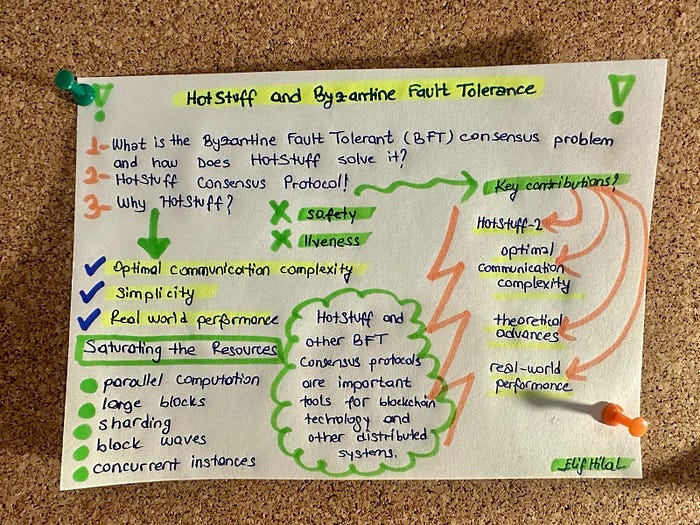
Why HotStuff?🎉
The “Why HotStuff” section of the article explains why HotStuff is such an important breakthrough in achieving consensus in distributed systems!
This section highlights several reasons why HotStuff is an important breakthrough in achieving consensus in distributed systems and why it should be used. Allow me to explain, my dear reader:
🏆 Here are some of the key points:
1. Optimal communication complexity: HotStuff is the first practical solution to the classical Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus problem with optimal communication complexity. This means that it is able to achieve consensus with minimal communication overhead, making it a highly efficient solution.
2. Simplicity: HotStuff’s simplicity has driven adoption as a standard for blockchain design, and many variants and improvements have been built on top of it. Its simple design makes it easy for developers to understand and implement.
3. Real-world performance: The article notes that HotStuff’s performance in real-life settings has been impressive, with many blockchain systems adopting it as a golden standard for blockchain design.
As a breakthrough algorithm in achieving consensus in distributed systems, HotStuff is an important tool for developers working with blockchain systems and other distributed systems.
If you don’t have any questions about these issues, I’ll continue to explain. I will make sure it is all clear and understandable. Stick with me!
What are the Key Contributions from HotStuff?🎄
A few key contributions from HotStuff:
This means it can reach consensus with minimal communication overhead, making it a highly efficient solution.
2. Theoretical advances: HotStuff has enabled many theoretical advances, including several models where HotStuff-based solutions close problems that have been open for decades.
3. Real-world performance: HotStuff’s simplicity has driven adoption as a standard for blockchain design, with many variants and improvements on top of it.
Its real-world performance was impressive, with many blockchain systems adopting it as the gold standard for blockchain design.
4. HotStuff-2: A recent observation called HotStuff-2 showed that improving the original HotStuff latency by up to 33% without sacrificing any desired features is possible.
Overall, these important contributions highlight the importance of HotStuff as a groundbreaking algorithm for achieving consensus in distributed systems.
As you can see, with its optimal communication complexity, theoretical advances, and real-world performance HotStuff is an essential tool for developers working with blockchain systems and other distributed systems.
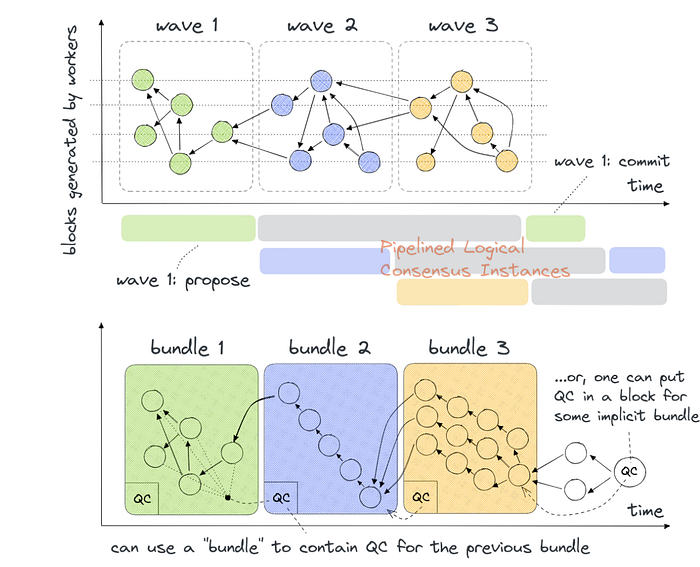
Saturating the Resources?🥇
“Saturating the Resources” refers to a technique for increasing throughput in a consensus protocol by offloading networking and computationally intensive tasks to workers.
Despite the sequential skeleton of a consensus protocol, certain tasks such as signature verification, mempool synchronization, and block dissemination can be made parallel between the key phases of consensus.
For example, in real-life HotStuff enabled systems, the leader node often has work offloaded to a farm of CPUs or even to a local cluster of hosts, each handling messages to/from other nodes and carrying verification in parallel. This technique can help increase the efficiency and performance of consensus protocols like HotStuff.
What are the Differences? 🎁
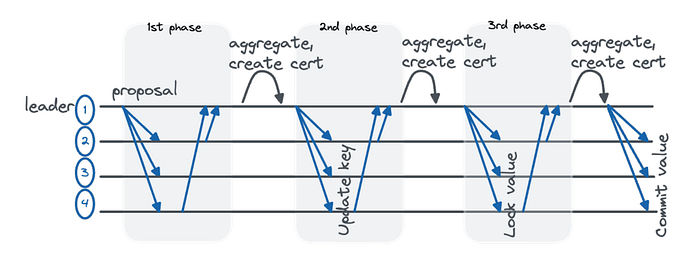
The HotStuff consensus protocol has several distinctive features when compared to other consensus protocols. Here’s a list of some of these key differences:
This means decisions are made after a “proposal,” “voting,” and “decision” phase. This structure allows HotStuff to reach consensus efficiently, even if some nodes are faulty or malicious.
This makes it more adaptable and faster in practice than some other protocols, which need to make conservative assumptions about network conditions.
This allows the system to remain efficient even if view-changes are frequent.
As a result, it’s much easier to ensure the security of a HotStuff-based system, because there are fewer places where bugs or other issues could hide.
For example, it can be combined with a protocol that offers fairness in terms of which node gets to propose the next block.
This means that the system does not rely on synchronized clocks and can still function efficiently when network delays occur.
Each of these points makes HotStuff a unique and robust consensus protocol for distributed systems, particularly for blockchains that need to operate securely and efficiently under real-world conditions.
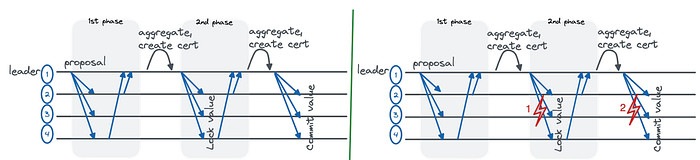
Two-Phase HotStuff? 🎗
Two-Phase HotStuff is a variant of the HotStuff consensus protocol that was introduced in a recent research paper. I love it! 🥰 This one is very interesting.
Two-Phase HostStuff was designed to achieve all five desirable properties of HotStuff with a two-phase view rather than a three-phase sub-protocol which you can see in detail in the graphic below.
The five desirable properties are:
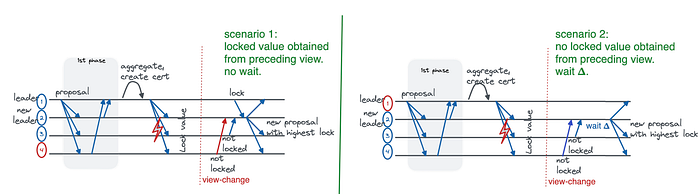
Two-Phase HotStuff demonstrates that achieving these properties with only two phases is possible, rather than the three phases required by the original HotStuff protocol.
This makes Two-Phase HotStuff more efficient and simpler to implement than the original protocol while still achieving the same desirable properties.
I want to share another helpful article that will help you to get even more detailed information on this subject:
In conclusion, HotStuff and other Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus protocols are critical tools for blockchain technology and other distributed systems.
HotStuff’s optimal communication complexity, theoretical advancements, and real-world performance have made it the gold standard for blockchain design. As such, developers can leverage this algorithm to create more efficient and secure blockchain systems.
As blockchain technology becomes increasingly widespread, tools like BFT consensus protocols will become ever more important.
And, don’t worry my dear reader, as I learn new information, I will continue to share it with you. You can count on me!
In the meantime, get informed, and join the community. Let’s train together: - Sign up for my meetups in Meetup (Turkish) and Meetup (English) - And don’t forget to join our Telegram channel (english), and Telegram Channel (turkish)
🌻👻 I hope the contents of my articles are beneficial to you. 🧑🎤👩🏼🎤 Do not hesitate to contact me 😉🎄Thats me, Elif Hilal! 🔮 Thank you for reading my articles and blog posts.